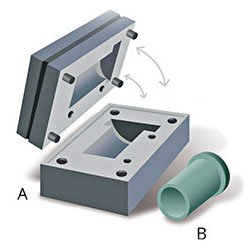
STEP 1 : Tooling and Pattern Making
Friendly neighbors there that’s where we meet can you tell
me how to get how to get to sesame street the movie
Investment casting has been used in various forms for the last 5,000 years. In its earliest forms, beeswax was used to form patterns necessary for the casting process. Today, more advanced waxes, refractory materials and specialist alloys are typically used for making patterns. Investment casting is valued for its ability to produce components with accuracy, repeatability, versatility and integrity in a variety of metals and high-performance alloys.
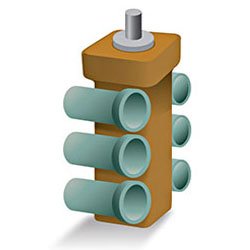
STEP 2 : Pattern Assembly
The wax patterns are assembled onto the sprue. The patterns are attached to a central wax stick, called a Runner,
to form a assembly.
Patterns used in sand casting may be made of wood, metal, plastics or other materials. Patterns are made to exacting standards of construction, so that they can last for a reasonable length of time, according to the quality grade of the pattern being built, and so that they will repeatably provide a dimensionally acceptable casting

STEP 3 : Dipping and Coating
Successive layers of ceramic (A) and stucco (B) are applied to the sprue assembly to form a hard shell. The shell is built by dipping the assembly in a liquid ceramic slurry and then into a bed of extremely fine sand. Up to eight layers may be applied in this manner.
The dipping and coating step in the investment casting process is one of the most crucial in ensuring the quality,
consistency and accuracy of finished castings. The sprue assembly is repeatedly dipped/coated with successive layers
of ceramic and stucco to build up a solid shell that will be the mold for the castings. Traditionally, this can be done hand, requiring much experience and skill.

STEP 4 : De-Waxing and Firing
The molds are flash-fired to remove the wax and sprue materials and then heated to 1,800° and placed on a sand bed, ready for pouring.
Dewaxing lubrication oil represents the largest use of scraped surface continuous crystallizers. Wax has the same boiling point range as lubricating oil fractions, but has a much higher freezing point. Therefore, cooling crystallization is a very effective way to separate the two materials.

STEP 5 : Melting and Pouring
The shell is filled with molten metal by gravity pouring. As the metal cools, the parts and gates and pouring cup become one solid casting
Investment casting is a manufacturing process in which a wax pattern is coated with a refractory ceramic material. Once the ceramic material is hardened its internal geometry takes the shape of the casting. The wax is melted out and molten metal is poured into the cavity where the wax pattern was.

STEP 6 : Knockout
The ceramic shell is broken off, the ceramic shell is broken off by vibration. and the individual castings are cut away.
You can get rid of that sledge hammer now and enter a new era of casting knockout. The FIS Knockout Machine
is specifically designed to quietly, safely, and efficiently remove the shell from an investment casting, and in a fraction of the time. If knockout is a problem for you, do yourself a favor and consider an FIS Knockout Machine. It may be the best investment decision you could make.
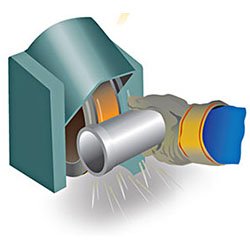
STEP 7 : Finishing
Excess metal is removed, surfaces are finished, and castings are heat treated. Traditionally, the parts are cut away from the central runner using a high speed friction saw, arc cutting, disc cutting or gas cutting.
As cast surface finish can be altered, corrosion resistant can be enhanced and improved by undertaking various post cast finishing processes. Investacast can provide a range of treatments which are carried out either on site or via our approved sub-contractors.
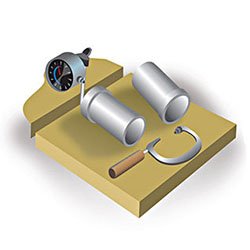
STEP 8 : Testing and Inspection
Castings undergo thorough testing and inspection to ensure that they meet dimensional tolerances and specifications.
Inspection and testing are performed before, during, and after manufacturing to ensure that the quality level of the product is within acceptable design standards.Whereas inspection is the activity of examining the product or its components to determine if they meet the design standards, testing is a procedure in which the item is observed during operation in order to determine whether it functions properly for a reasonable period of time

STEP 9 : Packing and Shipping
Castings are securely packaged for shipping to the customer.
Packing the finished investment castings to get them ready for coming delivery.
